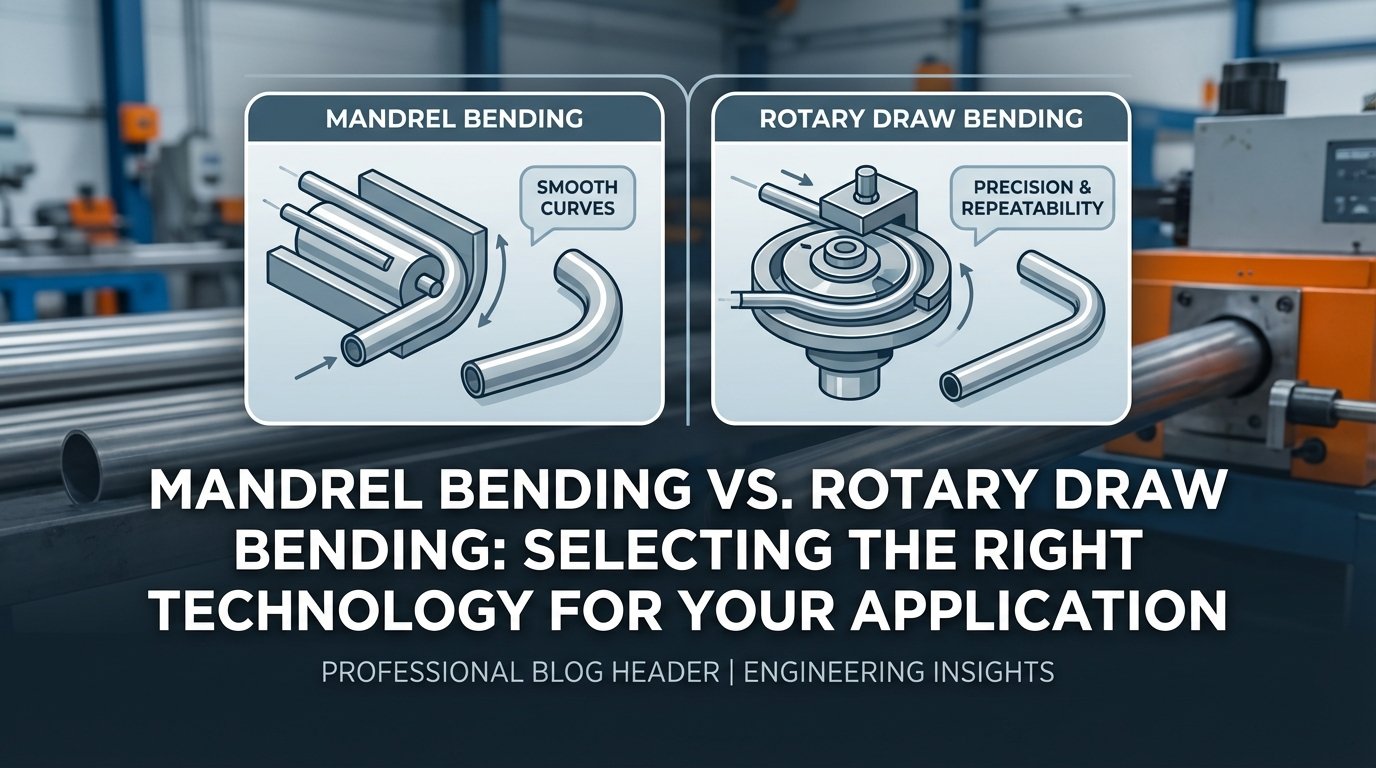
Aerospace Tube Bending Requirements: Meeting AS9100 Standards with Advanced CNC Technology
When a single bent tube failure can ground an aircraft or compromise mission-critical systems, aerospace manufacturers face quality demands unlike any other industry. AS9100 certification represents the baseline quality management standard for aerospace manufacturing, yet meeting these requirements for precision tube bending operations requires far more than documentation—it demands advanced CNC tube benders, rigorous process controls, and absolute dimensional repeatability.
The aerospace sector’s tube bending requirements extend beyond basic geometry. Every bend must maintain precise wall thickness, consistent radius tolerances, and documented traceability while working with specialized alloys like titanium, Inconel, and aerospace-grade stainless steel. Understanding how modern CNC tube bending technology enables AS9100 compliance provides engineering managers with the framework for selecting equipment that meets both regulatory requirements and production realities.
Understanding AS9100 Requirements for Tube Bending Operations
AS9100 builds upon ISO 9001 standards by adding aerospace-specific requirements that directly impact tube bending operations. These include configuration management, risk management, first article inspection protocols, and extensive process validation. For aerospace tube bending operations, several key requirements create distinct challenges:
- Traceability: Complete documentation from raw material certification through final inspection, including machine parameters for each bend
- Process validation: Statistical evidence that bending processes consistently produce parts within specification limits
- Calibration requirements: Regular verification of measurement equipment and machine positioning accuracy
- Special process controls: Tube bending qualifies as a special process where results cannot be fully verified by inspection alone
- Non-conformance management: Detailed procedures for identifying, documenting, and addressing out-of-specification parts
Modern precision tube bending machines equipped with advanced control systems directly support these requirements through integrated data collection, automated documentation, and real-time process monitoring. However, the equipment represents only one component of AS9100 compliance—the combination of capable machinery, validated processes, and trained personnel creates the quality framework aerospace applications demand.
Critical Tolerances in Aerospace Tube Bending
Aerospace applications impose tolerance requirements that challenge conventional tube bending capabilities. Hydraulic and fuel system components typically require bend angle tolerances of ±0.5 degrees or tighter, with centerline radius accuracy within ±0.010 inches. Wall thickness variation during bending must remain within 10% of nominal dimension, while ovality measurements cannot exceed specifications that often fall below 5% of tube diameter.
These demanding tolerances exist for legitimate engineering reasons. In hydraulic systems operating at 3,000+ PSI, dimensional inconsistencies create stress concentrations that can lead to fatigue failures. In fuel systems, geometry variations affect flow characteristics and can compromise performance or create safety hazards. Environmental control systems require precise tube geometry to ensure proper fit within tight airframe spaces where even millimeter-level deviations prevent installation.
Material Considerations and Spring-back Compensation
Aerospace tube bending frequently involves materials selected for strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, or high-temperature performance rather than formability. Titanium 3Al-2.5V, Inconel 625, and 15-5 PH stainless steel present significant bending challenges due to their high strength and substantial spring-back characteristics.
Advanced CNC tube benders address these challenges through programmed spring-back compensation algorithms that adjust bend angles based on material properties, bend radius, and wall thickness. These systems store material-specific parameters developed through first article qualification testing, then automatically apply appropriate compensation factors for production runs. This capability proves essential for AS9100 compliance, as it enables consistent first-piece accuracy without iterative trial-and-error adjustments that waste expensive aerospace materials.
CNC Technology Advantages for AS9100 Compliance
Modern aerospace tube bending machines incorporate CNC technology that fundamentally transforms quality assurance capabilities. Unlike manual or semi-automatic bending equipment, fully programmable CNC tube benders create the process control foundation necessary for AS9100 certification.
Repeatability and Statistical Process Control
Electric servo-driven CNC bending systems achieve positioning repeatability within ±0.001 inches, providing the mechanical precision aerospace applications require. This repeatability translates directly to part-to-part consistency measurable through statistical process control methods. When combined with automated measurement systems, CNC tube benders generate the Cpk data required to demonstrate process capability during AS9100 audits.
The control systems in advanced tube bending technology continuously monitor critical parameters including carriage position, rotation angle, clamp pressure, and mandrel position. Any deviation from programmed values triggers alarms before non-conforming parts are produced, supporting the preventive approach AS9100 emphasizes.
Digital Documentation and Traceability
Integrated control systems automatically generate production records that satisfy AS9100 traceability requirements. Each bent tube can be linked to specific machine programs, operator credentials, material lot numbers, and inspection results. This digital documentation eliminates manual data transcription errors while creating searchable records that support root cause analysis when quality issues emerge.
For aerospace tube bending machine dealer selection, this capability should represent a critical evaluation criterion. Systems that integrate with broader manufacturing execution systems (MES) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms provide seamless data flow from order receipt through final delivery, strengthening overall quality management system effectiveness.
Selecting Tube Bending Machines for Aerospace Applications
Aerospace manufacturers and their suppliers must evaluate multiple factors when specifying precision tube bending equipment for AS9100-compliant operations. The decision extends beyond basic bending capacity to encompass control sophistication, tooling flexibility, and support infrastructure.
Machine Capabilities Assessment
Aerospace tube bending demands machines capable of handling diverse tube diameters, wall thicknesses, and bend radii while maintaining tight tolerances. Key specifications include:
- Bend radius capability down to 1.5D (one and one-half times tube diameter) or tighter for compact assemblies
- Multi-stack tooling options enabling multiple bend radii without tool changes
- Mandrel systems appropriate for thin-wall tubing prone to collapse or excessive ovality
- Boost assistance for bending high-strength materials that exceed standard force capacity
- Right-hand and left-hand bending capability for complex geometries
Electric CNC tube benders increasingly replace hydraulic systems in aerospace applications due to superior positioning accuracy, reduced maintenance requirements, and elimination of hydraulic fluid contamination risks. Electric servo motors provide precise control of all bending axes with repeatability that hydraulic systems cannot match.
Control System Requirements
The controller represents the intelligence behind aerospace-grade tube bending machines. Modern systems should offer:
- 3D graphical programming with collision detection to prevent tooling crashes
- Automatic XYZ coordinate extraction from CAD models to minimize programming errors
- Material libraries containing spring-back compensation factors for common aerospace alloys
- Password-protected access levels preventing unauthorized program modifications
- Network connectivity for program transfer and production data collection
- Real-time monitoring with statistical process control charting capabilities
These control features directly support AS9100 requirements for configuration management, process validation, and continuous improvement. The programming interface should enable engineers to develop and verify bending programs offline, reducing machine downtime and supporting efficient new product introductions.
Tooling Considerations for Aerospace Specifications
Tooling quality directly impacts aerospace tube bending outcomes. Bend dies, clamp dies, pressure dies, mandrels, and wiper dies must maintain dimensional accuracy while withstanding production forces. Aerospace applications often justify premium tooling investments due to material costs and the consequences of scrap generation.
Hardened steel tooling provides extended service life when bending abrasive materials like titanium. Precision-ground surfaces minimize marking while supporting consistent bend quality throughout tool life. For high-volume production, tooling with replaceable wear components reduces long-term costs while maintaining specification compliance.
Mandrel selection particularly influences thin-wall tube bending success. Articulated mandrels with multiple balls provide superior support during tight-radius bends, preventing wrinkles on the intrados and excessive thinning on the extrados. The mandrel must be sized appropriately for specific tube dimensions and material characteristics—a detail that separates experienced aerospace tube bending machine dealers from generalist equipment suppliers.
Validation and First Article Inspection Protocol
AS9100 requires formal validation of tube bending processes before production authorization. This validation typically involves producing first article samples that undergo comprehensive dimensional inspection using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or optical measurement systems. The inspection verifies:
- Bend angles against drawing specifications
- Centerline radius dimensions
- Overall length and leg length measurements
- Rotation (clocking) between bends
- Wall thickness at critical locations
- Ovality measurements
- Surface condition and freedom from defects
Results are documented in First Article Inspection Reports (FAIR) that become part of the quality record. Advanced tube bending technology with measurement integration capabilities can perform in-process verification, identifying deviations before parts are removed from the machine. This immediate feedback supports rapid process optimization during validation phases.
Quality Control and In-Process Inspection
Maintaining AS9100 compliance during production requires ongoing quality verification beyond initial process validation. Production runs should incorporate statistical sampling plans appropriate to quantity and criticality. Some aerospace tube bending operations benefit from 100% inspection using automated measurement systems that verify critical dimensions without significantly impacting cycle times.
CNC tube benders with integrated measurement probes can perform in-cycle verification of bend angles and positions, automatically adjusting subsequent operations if drift is detected. This closed-loop control represents a significant advancement over traditional methods requiring post-process inspection and manual machine adjustment.
Training and Workforce Development
AS9100 explicitly requires that personnel performing special processes like tube bending be appropriately trained and qualified. Organizations must maintain training records demonstrating competency in machine operation, quality inspection procedures, and non-conformance identification.
When selecting an aerospace tube bending machine dealer, available training programs should factor into the decision. Comprehensive operator training, programmer instruction, and maintenance certification ensure the workforce can fully utilize equipment capabilities while supporting AS9100 compliance. American manufacturers with applications engineering support and responsive service organizations provide ongoing resources that extend beyond initial installation.
Meeting Defense and Space Program Requirements
Aerospace tube bending for military and space applications often involves additional requirements beyond AS9100. Defense programs may require ITAR compliance, restricting access to foreign nationals and imposing data security protocols. NASA programs incorporate unique material specifications and inspection requirements driven by mission-critical reliability needs.
Precision tube bending equipment manufactured in the United States by companies with proven track records serving defense and space programs offers advantages for these specialized applications. Domestic manufacturing simplifies ITAR compliance while supporting supply chain security. Established relationships with prime contractors and government agencies demonstrate capability to navigate complex quality and security requirements.
Implementing AS9100-Compliant Tube Bending Operations
Successfully integrating aerospace tube bending capabilities that meet AS9100 standards requires coordinated attention to equipment selection, process development, quality system integration, and workforce qualification. Organizations should approach implementation systematically:
- Define specific tube bending requirements including materials, geometries, and tolerance demands
- Evaluate CNC tube bending machines based on capability, control sophistication, and support infrastructure
- Select tooling appropriate for planned applications with consideration for future flexibility
- Develop detailed process documentation including machine parameters and inspection procedures
- Conduct thorough first article validation with comprehensive dimensional inspection
- Integrate tube bending operations into broader quality management system documentation
- Train personnel and establish ongoing competency verification procedures
- Implement continuous improvement processes using production data and quality metrics
This structured approach ensures tube bending operations support AS9100 certification while delivering the part quality aerospace applications demand.
Partner With Proven Aerospace Tube Bending Expertise
Meeting aerospace tube bending requirements demands more than capable equipment—it requires partnership with specialists who understand both the technology and the rigorous quality standards governing aerospace manufacturing. Whether establishing new capabilities or upgrading existing operations to meet evolving AS9100 requirements, selecting a knowledgeable aerospace tube bending machine dealer provides access to application engineering support, comprehensive training, and ongoing technical resources.
Organizations serving aerospace, defense, and space programs benefit from working with American manufacturers offering proven solutions backed by decades of experience with demanding applications. Contact our team to discuss your aerospace tube bending requirements and discover how advanced CNC technology supports AS9100 compliance while delivering the precision and repeatability your applications demand.